Osteoarthritis – a collective name of the dystrophic-degenerative disease joint guidance on the appliance of different localization and etiology, with this similar clinical and morphological of the painting and of the exodus and manifest the defeat of the joint cartilage, subchondral bone of the entities, capsules, ligamentous apparatus.
Osteoarthritis is the most common pathology is in rheumatology practice, according to the data of health statistics of them suffer up to 1/5 of the total population. Osteoarthritis is the cause of the significant reduction of the quality of life of approximately half of the patients, the greater part of which becomes disabled. The incidence is directly dependent on the age: osteoarthritis is unlikely that at an early age, he made his debut more often after 40-45 years of age and in people older than 70 years and radiological signs are defined in the great majority of cases. At the age of the prevalence of approximately 6.5%, after 45 years of 14-15%, after 50 years – from 27 to 30%, for people older than 70 years is 80 to 90%.
More often osteoarthritis is a pathological process involving small joints of the brush (the women 10 times more than men), the thumb of the foot intervertebral m? s joint thoracic and cervical parts of the spine, as well as the knee and hip and joints. Osteoarthritis of the knee and the hip joints, occupies a leading place, according to the degree of severity of the clinical manifestations and negative impact on quality of life.
For osteoarthritis is characteristic integral of the defeat of joint guidance and support of the equipment:
- inflammatory changes in the cartilage of the joint;
- participation in the process subject of the bone structure;
- synovitis – inflammation of the inner layer of the capsule of the joint;
- bursitis – the defeat of bags around the joints;
- reactive inflammation of the soft tissues (muscles, subcutaneous tissue, ligamentous apparatus), are to be found here, in the projection of the parts of the joint.
Given that the main cause of osteoarthritis are inflammatory changes in several of the western countries, it is called a disease of the arthritis. In the medicine the terms of arthritis and osteoarthritis is found here with the same frequency and involve the same pathological process. In the last time rheumatology practice more often is the term applied to oa, emphasizes the participation in the process, not only the amount of the joint, such as the balancing of the connection, but form the bones of the entities.
The consequences of osteoarthritis in the absence of proper treatment, are converted to a progressive decrease of the amplitude of motion in the affected joint, immobilizing.
Currently, the approach to the understanding of osteoarthritis has changed dramatically: the disease is considered as an aggressive process of destruction of the cartilage of the joint under the influence of the inflammation that leads to the active anti-inflammatory therapies.
Synonyms: arthritis, arthrosis, osteoarthritis, deforming osteoarthritis.
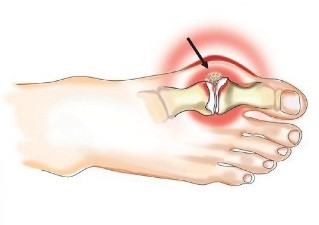
Causes and risk factors
In the scientific community there is some controversy about the causes of the defeat of the joints. Some researchers attribute a major role in damage to the cartilage covering the joint surfaces under the influence of multiple factors, which leads to the violation of the biomechanics of the joint and distróficosm changes in its environment, of the structures. Others, on the contrary, they see the root cause of the defeat of the layer surface, the mating structure of bone that form the joint (for example, due to a violation of the microcirculation), and the secondary of the changes believe that the dystrophy and degeneration of the cartilage.
The causal factors most common cause the development of osteoarthritis:
- previous acute traumatic joint damage (rupture or tearing of the ligaments, injury, dislocations, guided intra-articular fracture, penetrating wounds);
- harmful systematic loading, related to a specific activity (professional athletes, dancers, people involved in the work, a physical, etc);
- obesity;
- the local impact of low temperatures;
- chronic diseases, which suffers from some of the local microcirculation (endocrine pathology is pathology is the vascular bed, etc);
- dragged along the acute infectious diseases;
- the hormonal change (pregnancy, period menopausal);
- the autoimmune diseases that involve damage of connective tissue;
- connective tissue dysplasia (innate weakness of this type of tissue, accompanied by increased mobility of the joints);
- genetic pathology is the defect of a gene which is localized on chromosome 12 and encodes procollagen type II (COL2A1) or VDR gene which controls vitamin D-endocrine system;
- congenital structural and functional abnormalities of articular guided to the apparatus;
- mature, old and senile age;
- depression of the bone (treating osteoporosis);
- chronic intoxication (including alcohol);
- transferred to the operational engagements in the joints.
In most of the cases of osteoarthritis it has a poly-etiological nature, that is to say, develops sochetannom the effects of various causal factors.
The symptoms of osteoarthritis
For osteoarthritis is not common, acute, the clinical picture, changes in the joints are progressive, slowly ascending nature, which is manifested by the gradual strengthening of the symptoms:
- the pain;
- periodically comes the crunch in the affected joint;
- the deformation of the articulation of the nascent and growing as the development of the disease;
- stiffness;
- limitation of the mobility (reduction of the volume of active and passive movements in the affected joint).
The pain of osteoarthritis is convincing account of the transient nature, it appears in the movement, in the background of a great burden, at the end of the day (which can be so intense that it does not allow the patient to sleep). Permanent, non-mechanical nature of the pain of osteoarthritis corresponds to, and is a testimony about the presence of active inflammation (swelling, subchondral bone, synovium, ligamentous of the unit or of periarticular muscles).
Most patients take note of the existence of the so-called initials of the aches and pains that arise in the morning hours after awakening, or after a long period of inactivity, and that in the course of the motor activity. Many patients define the state as the need to "develop the joint" or "divergent".
For the arthritis characterized by morning stiffness, which has a clear location and is short (not more than 30 minutes), are sometimes perceived by patients as "the feeling of the jelly" in the joints. Perhaps the feeling of jamming, the stiffness.
During the development of the synovitis reactive to the main symptoms of osteoarthritis are joined:
- the pain and the local elevation of the temperature, which is defined when the palpation of the affected joint;
- the permanent character of the pain;
- the increase of the joint, in the as swelling of the soft tissues;
- progressive reduction of the amount of movement.
For osteoarthritis it is characteristic the increase of the joint, in the as swelling of the soft tissues.
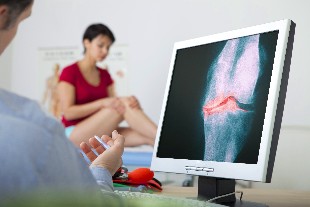
The diagnosis
The diagnosis of osteoarthritis is based on the evaluation of anamnestic data characteristic of the manifestations of the disease, the results of tool methods of research. Indicators of change, in general, and the biochemical analysis of blood for osteoarthritis is not common, appearing only when the active development of the inflammatory process.
The main tools in the diagnostic method of osteoarthritis is the x-ray, in the diagnosis obscure cases, it is recommended the realization of computer or magnetic resonance tomography.
Osteoarthritis of the knee and the hip joints, occupies a leading place, according to the degree of severity of the clinical manifestations and negative impact on quality of life.
For more methods of diagnosis:
- arthroscopy;
- ultrasound (evaluation of the thickness of the cartilage joint guidance, the synovial membrane, the status of the joint capsules, the availability of fluids).
- scan (assessment of the status of bone from the heads of the bones forming the joint).
The treatment of osteoarthritis
Medication therapy:
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents – outrage syndrome of pain and signs of inflammation at the time of aggravation;
- glucocorticosteroid hormones – intra-articular injection introduction for the outrage of the phenomena of synovitis; it is limited, in those cases in which you need in the shortest time possible to eliminate the painful symptoms;
- antifermental media (inhibitors of proteolysis) – prevent the progression of calcifications and degenerative processes in the cartilage and bone tissue;
- antispasmodics – to solve local muscle spasm in the damaged segment;
- anabolic medications speed up the regeneration of damaged tissues;
- the drugs aimed at the correction of the properties of the blood, the strengthening of the vascular walls, increasing the elasticity and regeneration of the tissues help to strengthen the walls of the vessels of microcirculation channel, providing good blood flow to the injured area;
- tools that improve the microcirculation;
- medications to the joints in spite of its massive distribution in the treatment of arthritis, in large placebo-controlled studies of clinical efficacy of this group of medications has not been tested.
Physical therapy of the applied methodology for the treatment of osteoarthritis:
- massage regional muscles, improves circulation and relieves spasm local;
- active kinesiotherapy, that is to say, performing exercises to osteoarthritis with the use of simulators;
- gymnastics osteoarthritis;
- lazeroterapiya;
- ultrasonic treatment;
- therapeutic baths, dirt, diesel; etc
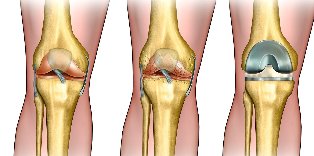
The ineffectiveness of any of these exposure methods, if there are complications turning to the operative treatment of osteoarthritis:
- the decompression of the goal of the epfisis and prolonged within the bone lock (decrease the intraosseous pressure in the affected area);
- corrective osteotomy;
- the total knee replacement of the joints.
In the early stages of the disease, applied mechanics, laser equipment (smoothing surface damage to the cartilage, the elimination of unviable plots). This effective method to relieves pain syndrome, but that is a temporary effect – 2 to 3 years.
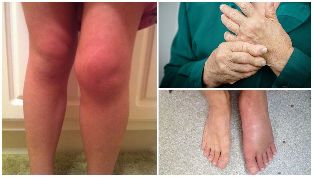
The possible complications and effects
The consequences of osteoarthritis, especially in the absence of a proper treatment, they become:
- progressive reduction of the amount of motion in the affected joint;
- immobilization.
Prognosis
The prognosis for life is favourable. Social benefit and labour of the prediction depends on the timeliness, the diagnosis and the start of treatment, is reduced to tighten the decision on the surgical treatment of the disease in case of need.
The prevention of the
- Exemption of charges, and length of the static tension of the affected joint.
- The use of orthotics, if necessary.
- The compliance of diet in osteoarthritis, the reduction of the mass of the body.
- Prevention of hypothermia.
- Complete the treatment of acute injuries to the joints until full recovery is compulsory rehabilitation.
- Dispensary observation of the signs of osteoarthritis.
































